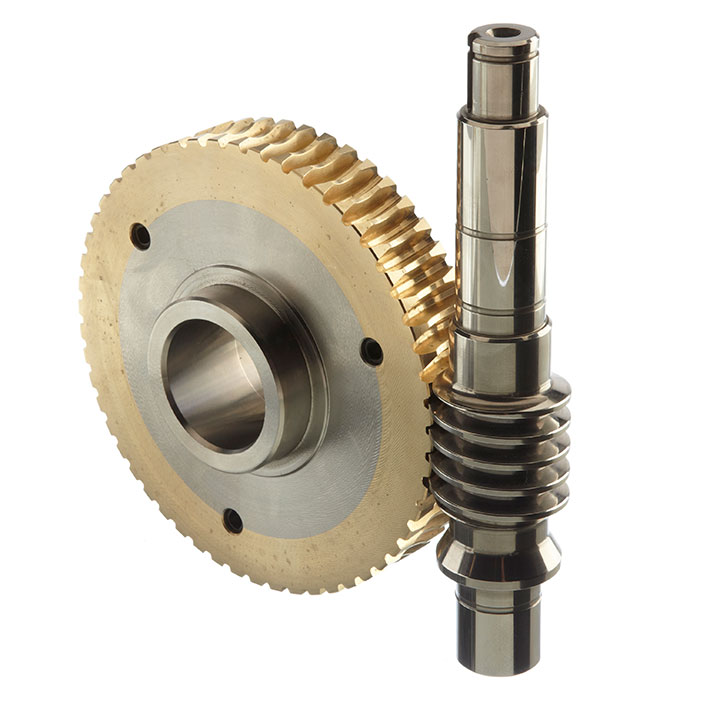
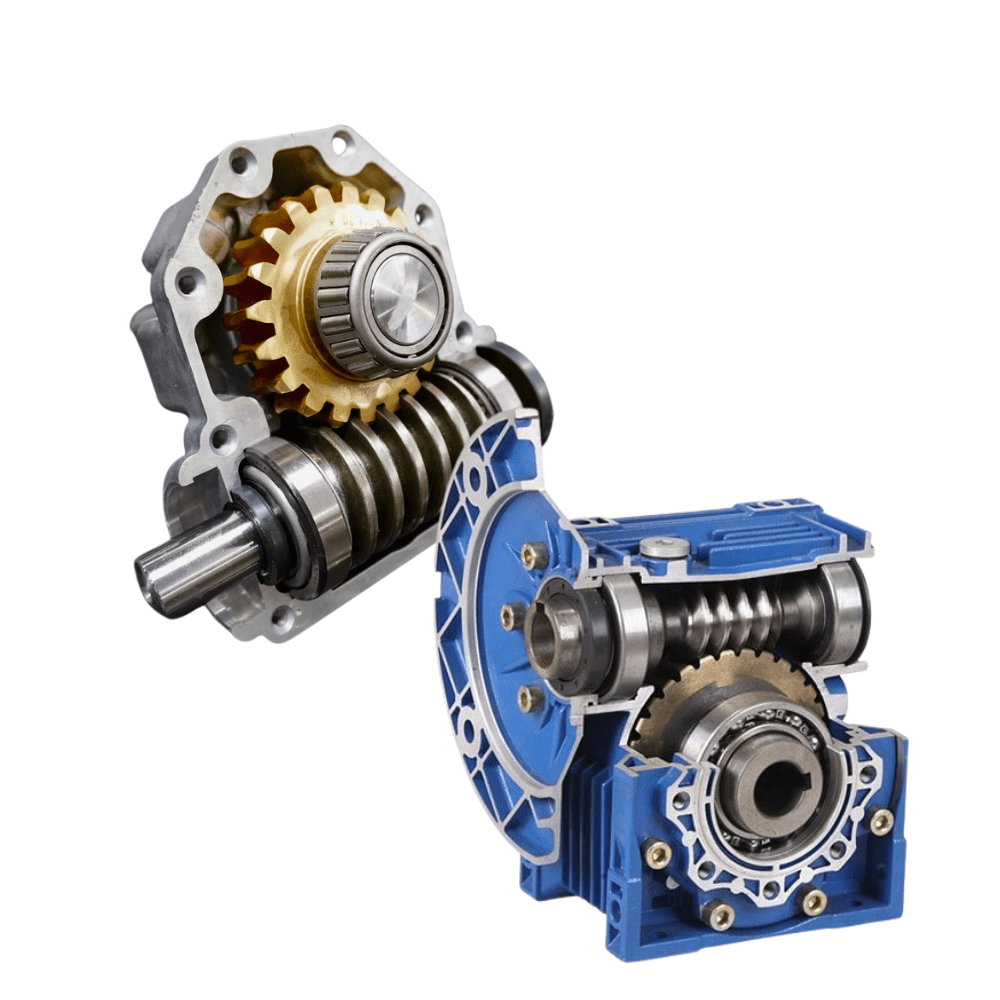
Product Description
DIY Worm Gear Wooden Wheel Bronze Precision Stainless Steering Micro Durable Globoid Pinion Plastic Helical Shaft Brass Suppliers Duplex Ground DIY Worm Gear
Application of Worm Gear
Worm gears are used in a wide variety of applications where high torque and low speed are required. Some of the most common applications include:
- Conveyors: Worm gears are used to power conveyors, which are used to transport materials in a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, food processing, and logistics.
- Pumps: Worm gears are used to power pumps, which are used to move fluids in a variety of applications, such as water treatment, wastewater treatment, and oil and gas production.
- Fans: Worm gears are used to power fans, which are used to circulate air in a variety of applications, such as heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC).
- Actuators: Worm gears are used to power actuators, which are used to move objects in a variety of applications, such as robotics, automation, and aerospace.
- Elevators: Worm gears are used to power elevators, which are used to transport people and goods between different floors of a building.
- Security gates: Worm gears are used to power security gates, which are used to control access to a building or area.
- Worm drive saws: Worm gears are used to power worm drive saws, which are used to cut wood, metal, and other materials.
Worm gears offer a number of advantages over other types of gear reducers, including:
- High torque: Worm gears can generate high torque, which makes them ideal for applications where heavy loads need to be moved.
- Low speed: Worm gears operate at low speeds, which makes them ideal for applications where smooth and controlled movement is required.
- Compact size: Worm gears are typically smaller than other types of gear reducers, which makes them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Low maintenance: Worm gears require very little maintenance, which makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Here are some of the limitations of worm gears:
- Low efficiency: Worm gears are not as efficient as other types of gear reducers, which can lead to increased energy costs.
- High noise levels: Worm gears can be noisy, which can be a concern in some applications.
- High maintenance costs: Worm gears require more frequent maintenance than other types of gear reducers, which can increase overall costs.
Despite these limitations, worm gears remain a popular choice for a wide variety of applications due to their high torque and low speed capabilities.
Here are some additional details about the applications of worm gears:
- Conveyors: Worm gears are used to power conveyors in a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, food processing, and logistics. The high torque of worm gears allows them to move heavy loads, such as boxes and pallets, smoothly and efficiently.
- Pumps: Worm gears are used to power pumps in a variety of applications, such as water treatment, wastewater treatment, and oil and gas production. The high torque of worm gears allows them to move fluids, such as water and oil, at high pressures.
- Fans: Worm gears are used to power fans in a variety of applications, such as heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC). The high torque of worm gears allows them to move air at high speeds, which helps to circulate air and keep people comfortable.
- Actuators: Worm gears are used to power actuators in a variety of applications, such as robotics, automation, and aerospace. The high torque of worm gears allows them to move objects, such as robotic arms and airplane flaps, smoothly and precisely.
- Elevators: Worm gears are used to power elevators in a variety of buildings. The high torque of worm gears allows them to move elevators smoothly and efficiently, even when they are carrying heavy loads.
- Security gates: Worm gears are used to power security CHINAMFG in a variety of buildings. The high torque of worm gears allows them to open and close security CHINAMFG smoothly and quickly, even when they are being held open by a person or object.
- Worm drive saws: Worm gears are used to power worm drive saws, which are used to cut wood, metal, and other materials. The high torque of worm gears allows them to make smooth, precise cuts.
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | – |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | – |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a worm gear?
A worm gear offers several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when selecting it for a specific application. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using a worm gear:
Advantages of using a worm gear:
- High gear reduction ratio: Worm gears are known for their high gear reduction ratios, which allow for significant speed reduction and torque multiplication. This makes them suitable for applications that require precise motion control and high torque output.
- Compact design: Worm gears have a compact design, making them space-efficient and suitable for applications where size is a constraint. The worm gear’s compactness allows for easy integration into machinery and equipment with limited space.
- Self-locking capability: One of the key advantages of a worm gear is its self-locking property. The angle of the worm thread prevents the reverse rotation of the output shaft, eliminating the need for additional braking mechanisms. This self-locking feature is beneficial for maintaining position and preventing backdriving in applications where holding the load in place is important.
- Quiet operation: Worm gears typically operate with reduced noise levels compared to other gear types. The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel teeth results in smoother and quieter operation, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired.
- High shock-load resistance: Worm gears have good shock-load resistance due to the sliding contact between the worm and the worm wheel teeth. This makes them suitable for applications that involve sudden or intermittent loads, such as lifting and hoisting equipment.
- Easy installation and maintenance: Worm gears are relatively easy to install and maintain. They often come as a compact unit, requiring minimal assembly. Lubrication maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity, but it is typically straightforward and accessible.
Disadvantages of using a worm gear:
- Lower efficiency: Worm gears tend to have lower mechanical efficiency compared to some other gear types. The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel teeth generates higher frictional losses, resulting in reduced efficiency. However, efficiency can be improved through careful design, quality manufacturing, and proper lubrication.
- Limited speed capability: Worm gears are not suitable for high-speed applications due to their sliding contact and the potential for heat generation. High speeds can lead to increased friction, wear, and reduced efficiency. However, they excel in low to moderate speed applications where high torque output is required.
- Heat generation: The sliding action between the worm and the worm wheel generates friction, which can result in heat generation. In high-load or continuous-duty applications, this heat buildup can affect the efficiency and longevity of the system. Proper lubrication and heat dissipation measures are necessary to mitigate this issue.
- Less suitable for bidirectional motion: While worm gears offer excellent self-locking capabilities in one direction, they are less efficient and less suitable for bidirectional motion. Reversing the direction of the input or output shaft can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the gear system.
- Lower accuracy in positioning: Worm gears may have lower accuracy in positioning compared to some other gear types, such as precision gear systems. The sliding contact and inherent backlash in worm gears can introduce some degree of positioning error. However, for many applications, the accuracy provided by worm gears is sufficient.
- Potential for wear and backlash: Over time, the sliding action in worm gears can lead to wear and the development of backlash, which is the play or clearance between the worm and the worm wheel teeth. Regular inspection, maintenance, and proper lubrication are necessary to minimize wear and reduce backlash.
When considering the use of a worm gear, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application and weigh the advantages against the disadvantages. Factors such as torque requirements, speed limitations, positional stability, space constraints, and overall system efficiency should be taken into account to determine if a worm gear is the right choice.
How do you ensure proper alignment when connecting a worm gear?
Ensuring proper alignment when connecting a worm gear is crucial for the smooth and efficient operation of the gear system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in achieving proper alignment:
- Pre-alignment preparation: Before connecting the worm gear, it is essential to prepare the components for alignment. This includes cleaning the mating surfaces of the gear and shaft, removing any debris or contaminants, and inspecting for any signs of damage or wear that could affect the alignment process.
- Measurement and analysis: Accurate measurement and analysis of the gear and shaft alignment are essential for achieving proper alignment. This typically involves using precision alignment tools such as dial indicators, laser alignment systems, or optical alignment instruments. These tools help measure the relative positions and angles of the gear and shaft and identify any misalignment.
- Adjustment of mounting surfaces: Based on the measurement results, adjustments may be required to align the mounting surfaces of the gear and shaft. This can involve shimming or machining the mounting surfaces to achieve the desired alignment. Care should be taken to ensure that the adjustments are made evenly and symmetrically to maintain the integrity of the gear system.
- Alignment correction: Once the mounting surfaces are prepared, the gear and shaft can be connected. During this process, it is important to carefully align the gear and shaft to minimize misalignment. This can be done by observing the alignment readings and making incremental adjustments as necessary. The specific adjustment method may vary depending on the type of coupling used to connect the gear and shaft (e.g., keyway, spline, or flange coupling).
- Verification and final adjustment: After connecting the gear and shaft, it is crucial to verify the alignment once again. This involves re-measuring the alignment using the alignment tools to ensure that the desired alignment specifications have been achieved. If any deviations are detected, final adjustments can be made to fine-tune the alignment until the desired readings are obtained.
- Secure fastening: Once the proper alignment is achieved, the gear and shaft should be securely fastened using appropriate fasteners and tightening procedures. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for torque values and tightening sequences to ensure proper clamping force and prevent any loosening or slippage.
It is worth noting that the alignment process may vary depending on the specific gear system, coupling type, and alignment tools available. Additionally, it is important to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for the particular gear and coupling being used, as they may provide specific instructions or requirements for alignment.
Proper alignment should not be considered a one-time task but an ongoing maintenance practice. Regular inspections and realignment checks should be performed periodically or whenever there are indications of misalignment, such as abnormal noise, vibration, or accelerated wear. By ensuring proper alignment during the initial connection and maintaining it throughout the gear’s operational life, the gear system can operate optimally, minimize wear, and extend its service life.
How do you calculate the gear ratio of a worm gear?
Calculating the gear ratio of a worm gear involves determining the number of teeth on the worm wheel and the pitch diameter of both the worm and worm wheel. Here’s the step-by-step process:
- Determine the number of teeth on the worm wheel (Zworm wheel). This information can usually be obtained from the gear specifications or by physically counting the teeth.
- Measure or determine the pitch diameter of the worm (Dworm) and the worm wheel (Dworm wheel). The pitch diameter is the diameter of the reference circle that corresponds to the pitch of the gear. It can be measured directly or calculated using the formula: Dpitch = (Z / P), where Z is the number of teeth and P is the circular pitch (the distance between corresponding points on adjacent teeth).
- Calculate the gear ratio (GR) using the following formula: GR = (Zworm wheel / Zworm) * (Dworm wheel / Dworm).
The gear ratio represents the speed reduction and torque multiplication provided by the worm gear system. A higher gear ratio indicates a greater reduction in speed and higher torque output, while a lower gear ratio results in less speed reduction and lower torque output.
It’s worth noting that in worm gear systems, the gear ratio is also influenced by the helix angle and lead angle of the worm. These angles determine the rate of rotation and axial movement per revolution of the worm. Therefore, when selecting a worm gear, it’s important to consider not only the gear ratio but also the specific design parameters and performance characteristics of the worm and worm wheel.
editor by CX 2023-11-08